Are you fully using the potential of your operational data? StorkJet introduces the Alerting module, which helps detect issues and sustain improvements.
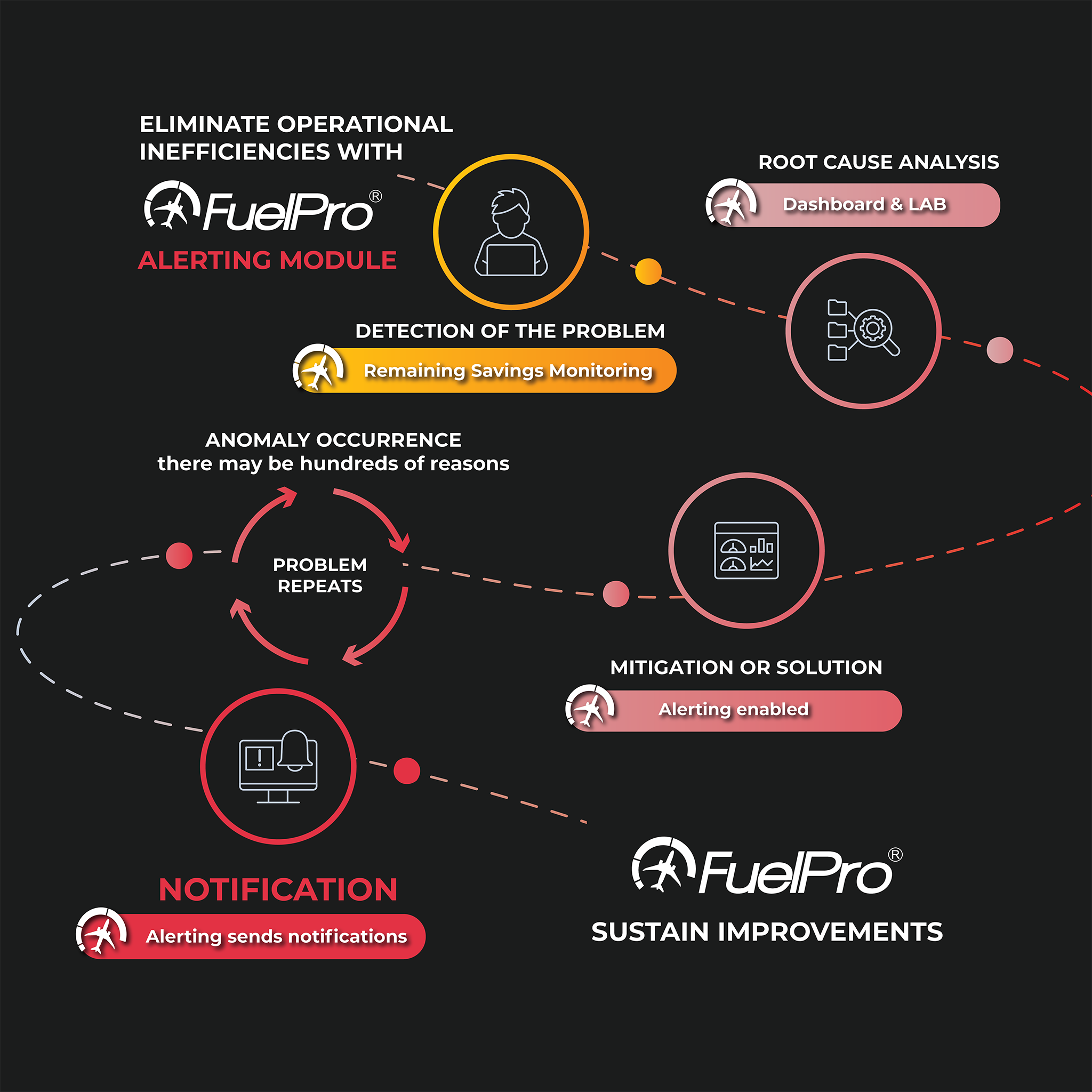
The Alerting Module is a FuelPro supporting product that keeps track of a wide range of parameters (anything you can think of!) for certain events, trends, and changes across different aggregation groups. When defined limits are exceeded, the module sends a detailed report regarding the occurrence to the given recipients.
It generates reports for outlying conditions that match the problem statement set by the operator’s complex needs. These reports provide analytical capability to different departments for identifying inefficiencies and addressing the root cause of the problem.
The module’s main goal is to achieve savings by resolving inefficiencies and improving Safety Performance Indicators (SPIs) through monitoring and analyzing data harvested from every corner of your operations. The complexity of aggregating data (tracking and filtering with aggregated parameters), the logic of trend change detection or event-based monitoring, report grouping with many identification parameters (datetime, sector, A/C type, tail number, flight number, etc.), and the multi-stakeholder perspective make the Alerting Module far ahead of its competitors in the market.
Let’s look at the following Customer Case to provide a more concrete definition.
Case 1: Overburn Attribution Matrix
One of our customers struggled with a high percentage of trip fuel overburn compared to the market average. It was a great opportunity for beta testing the Alerting Module. The goal was to monitor trip fuel overburn, identify root causes, and take action to improve safety and efficiency. Therefore, the airline’s Safety and OCC departments collaborated to define their „Overburn Attribution Matrix.”
StorkJet supported configuring an alert based on this matrix. Trip fuel overburn was monitored daily for defined limits per flight and weekly for the percentage of flights with overburn per sector. Flights with go-arounds and diversions were filtered out to reduce noise in the data. Supplementary parameters were provided as part of the matrix to allow deeper analysis of the root causes, such as:
- Landing Fuel Planned
- Landing Fuel Actual
- Low Visibility Operation (LVO) – Y/N
- Total Holding Time
- Cost-of-Weight (CoW) – Discretionary Fuel
- Diversion Fuel (Final Reserve + Destination Alternate Fuel)
- Performance Factors
- SID Overburn
- STAR Overburn
It’s important to note that the parameters in the attribution matrix were aggregated with their logic and required data from multiple sources to be parsed, processed, and matched. This technical complexity is essential for analyzing such a multifaceted problem.
The reports were distributed within a defined period to the relevant recipients. In this case, the Safety and OCC departments received slightly different reports that provided insights into the root causes of trip fuel overburn from different perspectives. It was discovered that certain sectors experienced frequent SID/STAR overburn due to overly optimistic planning. This led to increased discretionary fuel due to mistrust in the flight plan, deepening the issue because of the CoW of discretionary fuel.
As an action, planned SIDs and STARs at the airports with frequent overburns were replaced with more conservative ones. The issue was communicated transparently with pilots to address bias and reduce discretionary fuel, which also caused overburn.
On top of that, some cases of overburn were linked to long holding times at the destination airport due to unusual events (e.g., ATC strikes, NOTAMs, meteorological conditions, etc.). The reports helped OCC to raise awareness and make informed decisions regarding such situations.
After the integration, there has been a drastic drop (below market average) in overburn amounts, and percentages thanks to the planned SID and STARs change and communication with pilots. Additionally, the monitoring process remains in place to ensure the persistence of the solution. With the help of the Alerting Module, the airline not only reduced its overburn but also contributed to the improvement of SPIs.
Case 2: Climb – Fuel Consumption Inefficiency
One customer faced unexpected increases in fuel consumption during the climb phase, deviating from historical averages despite similar operational conditions. This anomaly presented a valuable opportunity for the Alerting Module to demonstrate its ability to isolate root causes while ensuring that external factors like weather and aircraft weight do not distort the analysis.
StorkJet configured an alert in the module to monitor the remaining savings of the „Climb – Vertical Profile,” a parameter pre-calculated in FuelPro. This parameter is calculated flight-by-flight by comparing actual and simulated fuel burn during climb. Simulation uses tail-specific performance models and assumes QAR initial conditions and weather. This approach enables precise „apple-to-apple” comparison reflecting operational changes in the actual profiles. Additionally, fuel KPIs, that are pre-calculated in FuelPro to support analysts, have been deployed as supplementary parameters to identify the root cause of the inefficiency.
The monitoring revealed that in an airport Air Traffic Control (ATC) began imposing step climbs during certain departures, requiring aircraft to maintain a 50 NM segment at FL 240 before continuing the climb. This operational adjustment significantly increased fuel burn during the climb phase for those flights, which negatively influenced the averages.
To address this, StorkJet provided detailed reports to the airline’s Flight Operations and OCC teams, highlighting affected sectors and quantifying the additional fuel burn. This insight enabled the OCC to review the routings with informed decisions to avoid the restriction when applicable. Additionally, they mitigated the inefficiency by optimizing cruise climb strategies when step climbs were unavoidable.
Following these interventions, the airline reduced mitigated imposed penalty for those departures. This demonstrated the Alerting Module’s precision and effectiveness in driving informed corrective actions, delivering long-term savings.